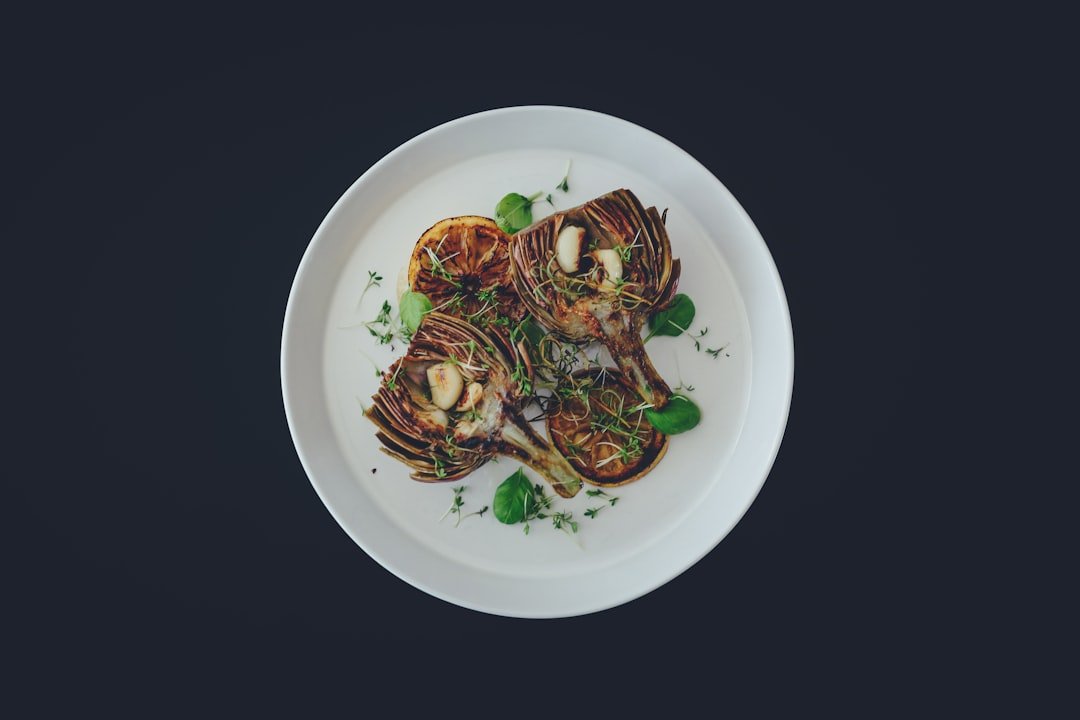
The Value of Food and Eating Food and eating are essential components of human life that go beyond simple sustenance to represent social interaction, cultural identity, and individual expression. Sharing a meal together has long been a fundamental part of family and community life, acting as a catalyst for enduring memories and fostering relationships. In many cultures, eating is more than just a meal; it’s a social ritual that strengthens bonds between people through common customs and experiences. Beyond the table, food plays a significant role in social structures, economic systems, and even political environments. Also, food has a significant impact on one’s identity. Certain foods or culinary customs are frequently linked to people’s personal histories, which can arouse feelings of nostalgia & community.
Key Takeaways
- Food and dining play a crucial role in bringing people together and fostering social connections.
- Cooking and culinary skills are not only practical but also a form of art that allows for creativity and self-expression.
- Dining culture has evolved over time, reflecting changes in society, technology, and globalization.
- Food is deeply intertwined with different cultures, serving as a means of preserving traditions and expressing identity.
- The impact of food on health and well-being is significant, highlighting the importance of making informed dietary choices.
Traditional recipes’ flavors & scents have the power to take people back to their early years or to important life events. Food thus becomes a narrative thread that permeates both individual & societal histories, thereby establishing it as a fundamental aspect of the human condition. Culinary Skills & Cooking The art of cooking is often considered an art form in which technique and creativity coexist.
Every technique and style used in the culinary arts reflects the culture and history from which it comes. In addition to knowledge of ingredients and methods, mastering the art of cooking also calls for an appreciation of food presentation. Eating becomes a multisensory experience as chefs and home cooks work to produce dishes that are not only tasty but also aesthetically pleasing.
A broad range of techniques are included in culinary skills, from fundamental knife skills to sophisticated cooking techniques like sous-vide or molecular gastronomy. As people learn to balance flavors, textures, and colors, experimentation and practice are frequently necessary steps on the path to becoming an accomplished cook. Anyone interested in cooking can now learn how to cook thanks to the democratization of culinary education brought about by the rise of cooking shows and online tutorials.
Because of its accessibility, home cooking has become more popular as people try to prepare meals that rival those found in restaurants in their own kitchens. The Development of Dining Culture Throughout history, globalization, technological breakthroughs, and shifting social mores have all had a major impact on dining culture. In the past, big parties were frequently held to celebrate important occasions or harvests, and communal feasting was a common practice.
The dining habits of societies changed as they developed. During the Renaissance, formal dining etiquette was introduced, signaling a change to more structured meal settings that placed an emphasis on presentation and manners. The dining culture of modern society is still changing quickly. The growth of casual dining & fast food is a reflection of shifting consumer preferences and the need for convenience.
However, there is also a growing trend toward farm-to-table & slow food, which emphasizes the value of local ingredients and sustainability. As people strive to strike a balance between convenience, quality, and authenticity, this dichotomy in dining culture serves as an example of the continuous balancing act between tradition and modernity. The Function of Food in Various Cultures Food is a potent symbol in many cultures, frequently reflecting social structures, values, and beliefs. Traditional foods are symbols of heritage & community in many societies, and they are closely linked to cultural identity. For example, pasta is more than just a common meal in Italy; it also symbolizes regional pride and family get-togethers.
Sushi, on the other hand, represents careful craftsmanship & reverence for seasonal ingredients in Japan. Also, religious observances & cultural festivals frequently heavily rely on food rituals. Food-themed festivals enable communities to unite in celebration while respecting their customs. For instance, Thanksgiving in the United States centers on a communal meal that highlights thankfulness, while Diwali in India is marked by a variety of sweets that represent wealth and happiness. People feel more connected to one another and a part of their culture thanks to these culinary traditions.
The Effects of Food on Health and Well-Being There is a complex and wide-ranging relationship between food and health. Energy levels and disease prevention are just two examples of how nutrition affects physical well-being. Overall health can be greatly improved by eating a balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. On the other hand, unhealthy eating habits can result in a number of conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Food has an impact on mental health in addition to physical health. Certain nutrients have been found to have an impact on mood & cognitive function.
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are present in fish, have been associated with better mental health outcomes, for example. Also, preparing & sharing meals can lower stress levels & promote emotional connections. Food thus provides sustenance for the mind and spirit in addition to the body. The Rise of Food Trends and Food Tourism In recent years, people’s attitudes toward dining experiences have been influenced by the enormous popularity of food trends. Gourmet street cuisine and plant-based diets are just two examples of how changing consumer tastes & social values are reflected in culinary trends.
This phenomenon has been greatly aided by social media platforms, which enable foodies to share their culinary explorations and learn about emerging international trends. With tourists looking to include genuine culinary experiences in their travels, food tourism has grown to be a significant part of travel culture. Travelers who want to experience local flavors and cooking methods are drawn to places with distinctive cuisines. Travelers are increasingly using culinary tours, cooking classes, and food festivals to fully experience a region’s culinary culture.
Through common culinary experiences, this trend not only boosts local economies but also promotes intercultural understanding. The Emotional and Social Aspects of Eating Eating is a social activity that unites people around a common table. Sharing meals together strengthens bonds between people & provides chances for interaction & camaraderie.
Meals frequently provide a setting for deep conversations that improve bonds, whether they are shared with family or friends. Dining can psychologically arouse a range of feelings associated with coziness and nostalgia. For many people, certain foods evoke pleasant memories or a sense of security.
A bowl of chicken soup, for example, can bring back memories of a family get-together during the holidays or a childhood home. This sentimental attachment to food emphasizes how it shapes social dynamics and individual identities. The Future of Food & Dining The food and dining scene will change along with society. From lab-grown meats to automated kitchens that expedite meal preparation, technological advancements have the potential to completely change how people interact with food. As people grow more conscious of how their food choices affect the environment, sustainability will probably continue to be a hot topic in culinary discussions.
Also, individualized nutrition based on each person’s unique health needs may become more important in the future. Biotechnology developments may make it possible to provide more accurate dietary advice based on lifestyle or genetic characteristics. The future holds exciting potential for how people interact with food as dining experiences continue to adjust to shifting consumer preferences, whether through virtual cooking classes or immersive dining concepts. In summary, food and eating are essential aspects of human existence that include social interactions, cultural significance, health effects, and changing trends. Whether cooking at home or trying out new restaurants, people’s culinary adventures add to the diverse fabric of global gastronomy that continues to influence societies everywhere.
Food and dining are closely tied to environmental issues, including the impact of climate change on food security. According to a recent article on ecoguardians.shop, the changing climate is posing significant challenges to global food production and distribution. This highlights the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as discussed in another related article on the same website here. By revolutionizing conservation efforts and prioritizing sustainability in the food industry, we can work towards a more secure and environmentally friendly future for food and dining.