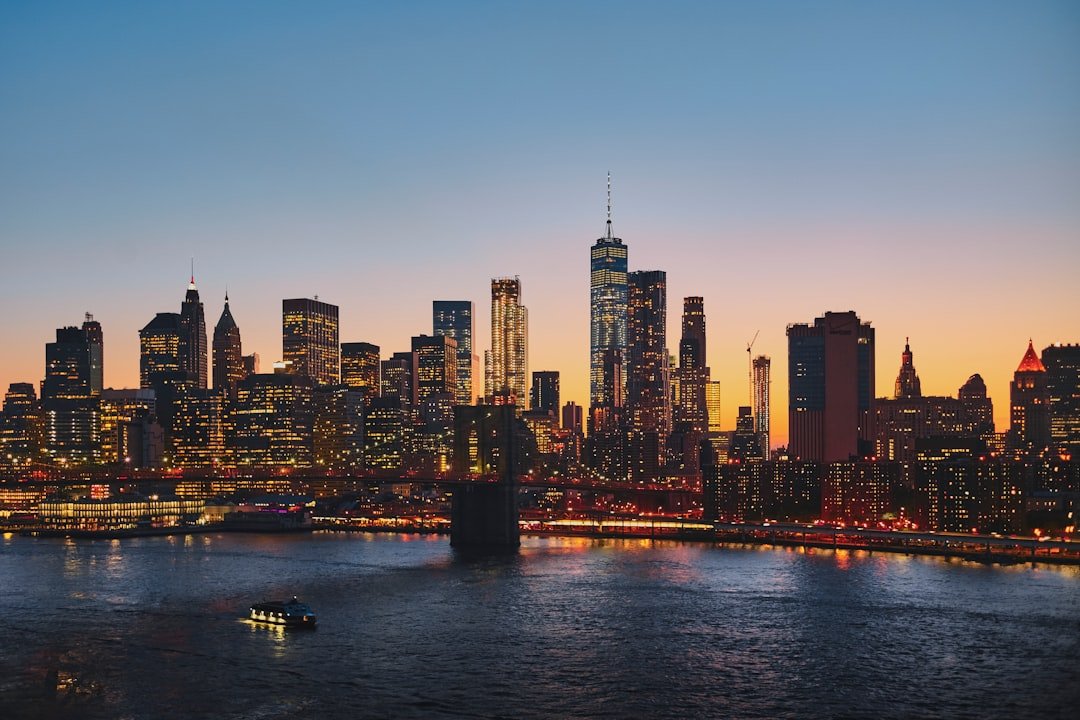
But in recent years, things have gotten significantly worse, with air pollution hitting dangerous thresholds that endanger both the environment and public health. A clear reminder of the ongoing crisis is provided by the city’s skyline, which is frequently covered in a dense haze.
Key Takeaways
- Beijing’s air pollution has reached dangerous levels, posing a serious threat to public health and the environment.
- The main causes of air pollution in Beijing include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and coal burning.
- Air pollution in Beijing has significant health impacts, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even premature death.
- The government has responded to the air pollution crisis with measures such as implementing stricter emission standards and promoting clean energy.
- Public awareness and activism play a crucial role in addressing Beijing’s air pollution problem, with citizens advocating for cleaner air and sustainable practices.
Particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations are reported to regularly surpass safe thresholds, causing public outcry and heightened scrutiny from both domestic and foreign observers. Beijing is a prime example of air pollution, which the World Health Organization (WHO) has identified as one of the major environmental health hazards in the world. The air quality index (AQI) can spike into the “hazardous” category on exceptionally bad days, causing advisories for vulnerable groups to remain indoors. Everyday life and transportation are impacted by the sharp decline in visibility in the city.
The need to address this crisis quickly becomes more evident as masks are worn by residents and air purifiers are used in many homes. Beijing’s fast industrialization and urbanization are major contributors to the city’s air pollution, which has many different causes. A major contributing factor is the excessive dependence on coal for energy generation. Coal continues to be a popular fuel despite initiatives to switch to cleaner energy sources, especially during the winter when demand for heating is at its highest.
Significant amounts of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter are released into the atmosphere during coal combustion, worsening the already terrible air quality. Vehicle emissions are a major contributor to the pollution problem, in addition to coal burning. In Beijing, traffic congestion is a daily occurrence due to the millions of vehicles on the road. Both nitrogen dioxide and PM2.5 are raised as a result of these vehicles’ exhaust.
| Location | Pollutant | Level |
|---|---|---|
| Beijing | PM2.5 | Dangerous |
| Beijing | PM10 | Very High |
| Beijing | Ozone | Unhealthy |
Also, the city’s construction projects produce dust and other pollutants that worsen the quality of the air. Because many industries function with inadequate environmental regulations, industrial emissions from factories in and around Beijing also play a significant role in the issue. Beijing’s air pollution has serious and wide-ranging effects on people’s health.
According to studies, extended exposure to high air pollution levels can cause a number of respiratory illnesses, heart issues, and even early mortality. Given the higher prevalence of asthma & other respiratory disorders among these groups, children & the elderly are especially at risk. Living in a polluted environment can have psychological effects as well; residents frequently experience stress and anxiety related to health issues. Also, air pollution has an enormous financial cost.
Public health systems are strained, and productivity is impacted by the medical expenses of treating illnesses linked to pollution. Air pollution costs China about $1 trillion a year in lost labor productivity & medical costs, according to a report from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This financial burden emphasizes how urgently effective interventions are needed to reduce air pollution & safeguard public health. A number of actions have been taken by the Chinese government to improve Beijing’s air quality in response to the worsening air pollution crisis. Stricter emissions regulations for automobiles and industries have been one of the most important initiatives.
In an effort to lessen dependency on fossil fuel-powered vehicles, the government has also made significant investments in the infrastructure of public transportation, encouraging the use of electric buses & subways. Also, Beijing has started campaigns to persuade citizens to switch to more environmentally friendly habits like walking or riding bicycles rather than driving. In addition, the government has taken action to gradually replace coal-fired power plants with renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
These initiatives show how sustainable development—which places equal emphasis on environmental health and economic growth—is becoming increasingly recognized. Thanks to social media & easier access to information, public awareness of Beijing’s air pollution has grown significantly in recent years. People are speaking out more about their concerns as they become more aware of the risks associated with poor air quality. Residents are organizing campaigns to demand government accountability and action, leading to the emergence of grassroots movements advocating for cleaner air.
From public protests to online petitions, activism has taken many different forms. In promoting policy changes and increasing public awareness of the negative health effects of air pollution, environmental NGOs have been instrumental. Local authorities are under pressure to give environmental issues top priority and consult with the public on possible solutions as a result of the growing public conversation surrounding air quality. Because of the international attention Beijing’s air pollution problem has received, China and other nations are working together to address environmental issues. Numerous international organizations have contributed their technical know-how and assistance in creating efficient air quality management plans.
For example, collaborations with agencies such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) have made it easier to share best practices for cutting emissions. Also, Beijing officials have heard from cities around the world that are dealing with comparable issues. Innovative strategies for combating air pollution have resulted from this exchange of ideas, including the adoption of green urban planning programs and the purchase of clean technology.
In addition to strengthening local initiatives, international cooperation promotes a sense of shared responsibility for halting climate change and enhancing air quality. Looking ahead, tackling Beijing’s air pollution issue will necessitate a multipronged strategy that incorporates community involvement, technological innovation, and policy reform. Increasing investments in solar, wind, & hydroelectric power can drastically reduce dependency on coal, making the switch to renewable energy sources crucial. Also, lowering emissions will be facilitated by improving building and industrial energy efficiency.
Also, by serving as organic pollutants’ filters, more green space in cities can contribute to better air quality. Vehicle emissions and traffic congestion can be decreased by urban planning that places a high priority on walkability and public transportation. Promoting a culture of environmental stewardship will also require educating the public through campaigns about sustainable practices. Beijing’s air pollution problem is more than just an environmental one; it also affects social justice, economic stability, and public health.
Since air pollution fuels climate change & transboundary pollution problems, the consequences of ignoring this crisis go beyond the city limits and affect China & even the world. It is impossible to exaggerate the significance of clean air; it is essential to both individual and community health. Beijing can improve the lives of its citizens and set an example for other cities dealing with comparable issues by giving priority to efforts to reduce air pollution.
Ultimately, resolving this urgent problem is necessary to promote a sustainable future in which the planet and people can coexist peacefully.
Beijing’s air pollution levels have been a major concern for years, prompting global initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. According to a recent article on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, countries and industries are working together to combat climate change and improve air quality. This effort is crucial for the health and well-being of Beijing’s residents, as well as for the planet as a whole.