Off-Grid Renewable Energy Solutions for Rural Communities Off-grid renewable energy solutions have become an essential lifeline for rural communities, especially in areas where traditional energy infrastructure is either nonexistent or unreliable. As a sustainable substitute for fossil fuels, these solutions use natural resources like sunlight, wind, & biomass to produce electricity. By providing a dependable energy source, off-grid systems can empower communities in many rural areas with little to no access to the national grid.
Key Takeaways
- Off-grid renewable energy solutions are crucial for providing electricity to rural communities without access to traditional grid systems.
- Advantages of off-grid renewable energy solutions include increased reliability, reduced environmental impact, and lower long-term costs compared to traditional grid systems.
- Types of off-grid renewable energy solutions available for rural communities include solar power, wind power, micro-hydro power, and biomass energy.
- Challenges to implementing off-grid renewable energy solutions in rural areas include high upfront costs, limited technical expertise, and lack of supportive policies and regulations.
- Successful case studies of off-grid renewable energy projects in rural communities demonstrate the positive impact on economic development, improved living standards, and environmental sustainability.
This autonomy from centralized power systems promotes social & economic advancement in addition to improving energy security. Also, off-grid renewable energy has importance beyond just producing electricity. Through facilitating access to basic services like clean water, healthcare, & education, it significantly contributes to raising the standard of living for locals. For example, solar panels can power schools & clinics, guaranteeing that these establishments stay open even in remote areas, and solar-powered water pumps can supply irrigation for agriculture.
Off-grid renewable energy solutions help close the living standards gap between urban and rural areas and promote sustainable development by meeting the particular energy requirements of rural communities. Dependability & Independence in Energy Use. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, enable communities to produce their own electricity, decreasing their dependency on outside sources and increasing their ability to withstand disruptions. For rural areas, where obtaining dependable energy can be extremely difficult, this is especially important. Off-grid solutions’ affordability. Over time, off-grid renewable energy systems may prove to be more economical.
Even though the initial outlay might be greater than that of joining the grid, traditional systems’ continuing maintenance & fuel expenses can mount up over time. However, once installed, off-grid solutions—especially those that run on solar or wind energy—have very low operating costs. Advantages for Rural Families. For low-income rural households, this financial advantage can be especially helpful because it frees up funds for other necessities like healthcare and education.
| Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Number of households powered | 10,000 |
| Energy access rate | 85% |
| Renewable energy sources used | Solar, wind, hydro |
| CO2 emissions reduced | 500 tons/year |
These households can enhance their general quality of life and make investments in their future by lowering their energy costs. In conclusion. With many advantages for rural communities and households, off-grid renewable energy solutions offer a practical and sustainable substitute for conventional grid systems. Depending on their unique requirements and available resources, rural communities can choose from a range of off-grid renewable energy options.
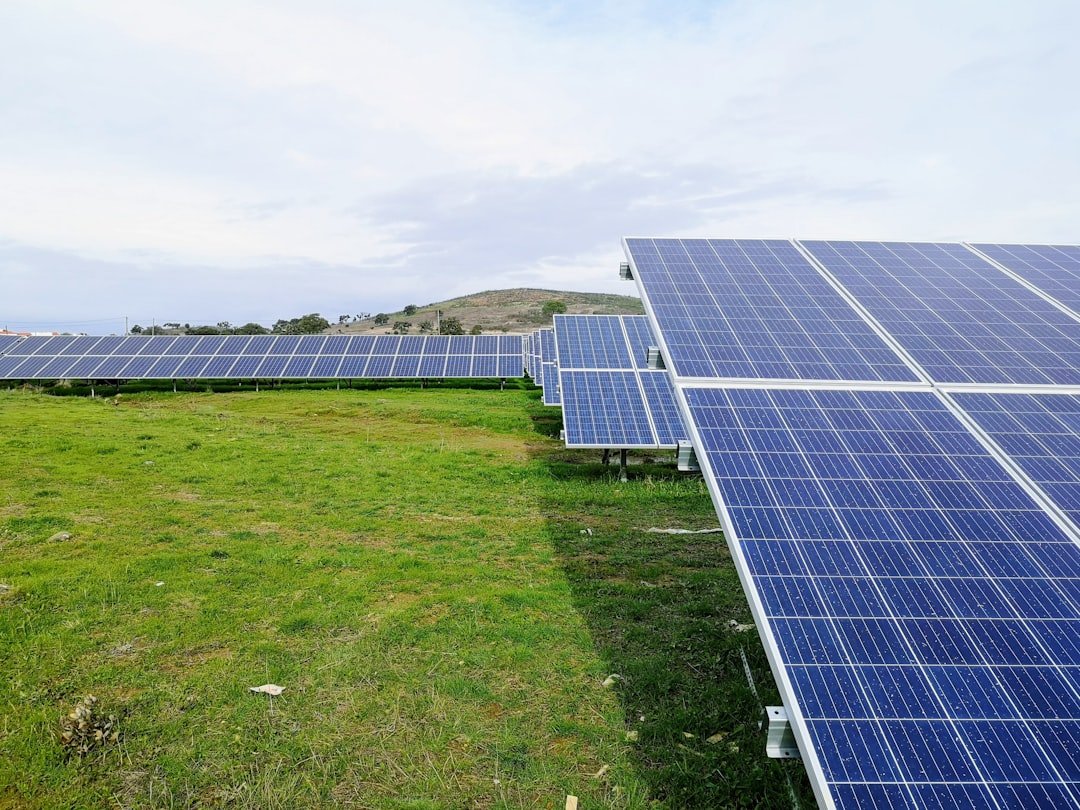
One of the most widely used alternatives is solar energy because of its adaptability and falling prices. Community solar farms or rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) panels can supply electricity to homes, businesses, & educational institutions. Solar water heaters can also provide hot water for household or agricultural purposes. For rural areas with adequate wind resources, wind energy is an additional feasible choice.
Installing small wind turbines can produce electricity for community grids or individual homes. When there is little sunlight, these systems can be used in conjunction with solar installations to provide a dependable energy source. For rural communities, especially those involved in agriculture, biomass energy offers a chance. Communities can manage waste & produce a sustainable energy source at the same time by turning organic waste into biogas or biofuels.
Off-grid renewable energy solutions offer many advantages, but their widespread adoption in rural areas is hampered by a number of issues. The upfront financial outlay needed for installation is one major obstacle. Many rural communities may not have the funds to invest in renewable technologies, or they may not have access to financing options.
Communities may be prevented from switching to sustainable energy sources by this financial barrier. A further obstacle is the absence of technical know-how and proficiency in renewable energy systems. There may be issues with performance & dependability in many rural areas due to a lack of qualified professionals to install and maintain these technologies. Also, social or cultural barriers might influence how well new technologies are accepted in the community. Targeted outreach and education initiatives are needed to overcome these obstacles by educating locals about the advantages of off-grid renewable energy sources and how to incorporate them into their daily routines.
Rural communities can be transformed by off-grid renewable energy solutions, as demonstrated by a number of successful case studies. The Solar Sister program in Africa is a noteworthy illustration of this, as it enables female entrepreneurs to distribute solar products within their communities. By offering assistance and training, Solar Sister has improved access to clean energy for households that previously used kerosene lamps and empowered women to take on leadership roles in their local markets. Another interesting case study is the Indian village of Dharnai. The community installed a solar microgrid system to power homes, businesses, and schools after years of unreliable electricity. In addition to supplying much-needed electricity, this project promoted local economic growth by making it possible for small businesses to run more effectively.
Dharnai’s success has sparked similar projects all over India, demonstrating the potential of off-grid renewable energy to strengthen rural communities. In rural areas, governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are essential in advancing off-grid renewable energy solutions. In order to increase access to clean energy through grants, subsidies, and technical assistance, numerous nations have put in place policies & programs. To help low-income families afford solar panels or wind turbines, for example, some governments provide financial incentives to households that make these investments. NGOs also make a substantial contribution by carrying out initiatives that offer resources and training to communities interested in embracing renewable energy sources.
In off-grid communities, groups like the Global Off-Grid Lighting Association (GOGLA) strive to promote solar lighting products, enhancing residents’ safety & standard of living. The development of sustainable energy solutions that address the particular requirements of rural populations requires cooperation between local communities, NGOs, and governments. Off-grid renewable energy solutions have significant and far-reaching effects on the economy & society. These systems allow rural communities to participate in revenue-generating activities that were previously unfeasible without dependable electricity.
Businesses can use electric lighting to extend their hours of operation, for instance, and agricultural operations can use contemporary equipment for processing & irrigation. Residents’ quality of life may improve and jobs may be created as a result of this increased economic activity. Socially, having access to off-grid renewable energy improves both adult and child learning opportunities.
Reliable electricity enables schools to offer previously unattainable digital learning resources or evening classes. Also, maintaining necessary medical equipment & making sure vaccines are stored at the right temperature are two ways that healthcare facilities with renewable energy sources can provide better services. Residents feel more empowered and proud of their community as a result of the general improvement in quality of life. Off-grid renewable energy solutions in rural areas seem to have a bright future as long as costs continue to drop & technology keeps improving.
With the increasing affordability and efficiency of innovations like battery storage systems, communities can now store excess energy produced during periods of peak production for use during times of low generation. By improving their dependability, this feature increases off-grid systems’ attractiveness to prospective customers. Hybrid systems that integrate several renewable energy sources, like solar, wind, and biomass, are also gaining popularity as a way to produce more resilient energy solutions that are suited to regional conditions.
Rural communities are realizing the significance of shifting from fossil fuels to sustainable alternatives as climate change awareness grows. This change offers chances for cooperation between community organizations, private sector investors, and local governments to create all-encompassing plans that support off-grid renewable energy sources. Ultimately, off-grid renewable energy solutions have the potential to revolutionize rural communities by offering dependable power sources that boost economic growth & raise living standards. Successful case studies show that cooperation and creativity can overcome the financial and technical obstacles that still exist.
The future appears bright for rural communities looking for sustainable energy solutions that empower their citizens and build resilience against outside challenges as long as governments & non-governmental organizations continue to support these initiatives.