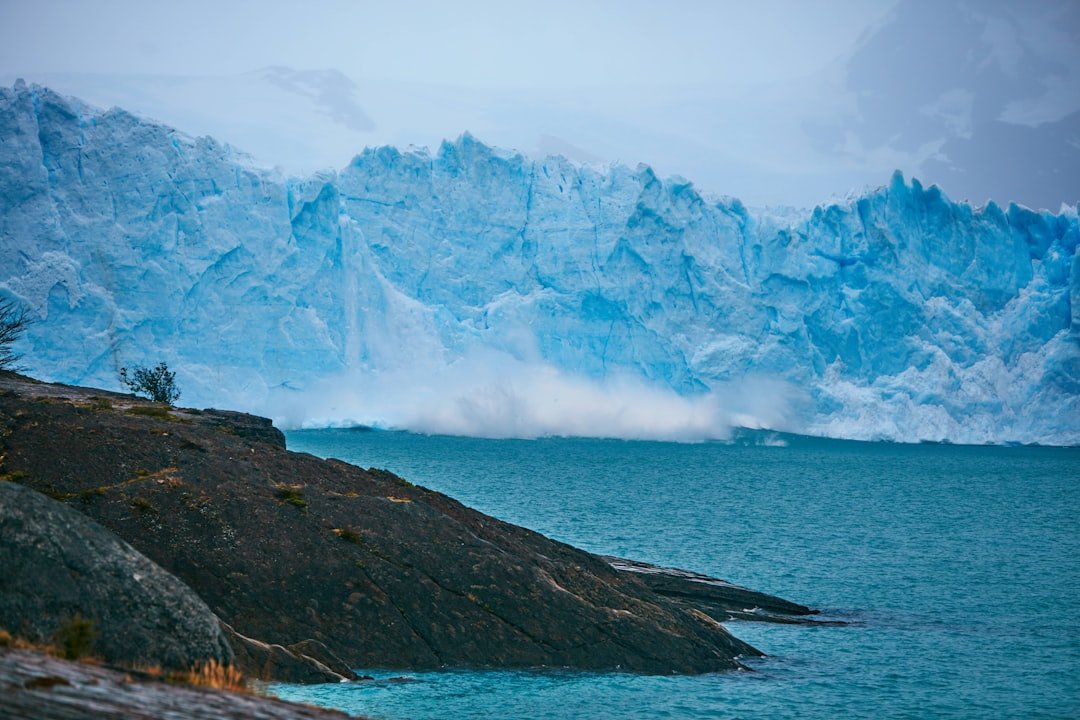
A Detailed Overview of Glacial Retreat The phenomenon of glaciers and ice sheets losing mass and volume, mostly as a result of rising global temperatures, is known as glacial retreat. This process has been seen all over the world and has important ramifications for human society and the environment. Glaciers that have existed for thousands of years are drastically thinning as a result of global warming, causing a series of changes that impact both nearby and far-off areas. These enormous ice formations’ retreat is a clear sign of climate change and concrete proof of the earth’s warming.
Key Takeaways
- Glacial retreat is the process of glaciers shrinking and melting due to rising temperatures, leading to significant environmental and societal impacts.
- Environmental consequences of glacial retreat include the loss of habitat for various species, changes in water quality, and increased risk of natural disasters such as floods and landslides.
- Glacial retreat contributes to sea level rise, posing a threat to coastal communities and infrastructure around the world.
- Wildlife and ecosystems are heavily impacted by glacial retreat, with species facing habitat loss, altered migration patterns, and increased competition for resources.
- Glacial retreat also has societal and economic impacts, including the loss of freshwater resources, increased risk of water scarcity, and challenges for industries reliant on glacier-fed rivers. Mitigation and adaptation strategies are crucial for addressing the effects of glacial retreat.
Glacial retreat has many different causes, including both man-made & natural ones. Glacier dynamics have always been impacted by natural climate variability, but the current rate of retreat is unprecedented & directly related to human activity, specifically the burning of fossil fuels & deforestation. Accelerated melting results from the disruption of the delicate balance that keeps glaciers stable caused by rising greenhouse gas emissions. To fully appreciate the wider effects of climate change and the pressing need for action, one must have a solid understanding of glacial retreat.
Landscapes are changing. Valleys are reshaped & new geological features are created as a result of the glaciers’ retreat, which reveals previously hidden land. This change may result in more sedimentation and erosion in neighboring lakes and rivers, which would impact aquatic habitats and water quality. disturbance of ecosystems.
Invasive species have the potential to disturb local ecosystems & endanger native plants and animals on the recently exposed land. Also, local climate changes are influenced by glacial retreat. A region’s temperature and precipitation patterns are greatly influenced by its glaciers. effects on regional ecosystems.
| Glacial Retreat Impact | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Sea Level Rise | 3.3 millimeters per year |
| Loss of Habitat | Threat to polar bears, penguins, and other species |
| Water Supply | Impact on availability of freshwater resources |
| Climate Change | Contribution to global warming and extreme weather events |
As their numbers decline, the cooling effect they offer is lost, which could result in warmer temperatures and changed weather patterns. Changes to animal migration patterns and plant growth cycles are just two examples of the ripple effects this shift may have on nearby ecosystems.
Sea level rise is one of the most important effects of glacial retreat.
The water that was previously frozen in glaciers flows into the oceans as they melt, expanding their volume. Large ice sheets, like those in Greenland & Antarctica, are melting quickly in polar regions, making this process especially noticeable there. The consequences of sea level rise are severe, endangering ecosystems and coastal communities globally. Because of things like local geology, land subsidence, & ocean currents, the effects of sea level rise differ from one place to another. Cities along the coast are especially at risk from erosion, flooding, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater supplies.
In certain places, entire communities might have to move because their houses are no longer livable. The financial consequences of these changes are enormous; estimates indicate that disaster relief and infrastructure adaptation will require billions of dollars. Wildlife & ecosystems that rely on cold climates are significantly impacted by glacial retreat. Due to the special habitats that ice & snow have produced, many species have adapted to live in glacial areas.
Biodiversity declines as a result of these habitats becoming smaller or nonexistent as glaciers retreat. Particularly vulnerable species include seals, polar bears, and some fish species, whose habitats are being lost or fragmented. Glacier retreat can alter food webs & ecological interactions in addition to directly destroying habitat.
For example, when glaciers melt, freshwater is released into lakes and rivers, changing the salinity and impacting aquatic life. For many species, temperature variations can also affect migratory and breeding patterns. Because ecosystems are interconnected, the effects of glacial retreat may have unanticipated repercussions for human and wildlife populations that depend on these ecosystems for survival by causing ripple effects through food chains.
Glacial retreat has far-reaching social effects on communities that depend on glaciers for cultural significance, tourism, and water resources. For millions of people, glaciers provide essential freshwater resources in many areas. Water availability is becoming more unpredictable as these glaciers recede, which could result in disputes over water rights and use. Food insecurity may worsen if communities that rely on glacial meltwater for agriculture struggle to maintain crop yields.
Economically, tourism sectors that depend on winter sports & picturesque scenery may be severely impacted by the retreat of glaciers. Insufficient snow cover or unappealing views due to glacier retreat could result in fewer visitors and lower profits for ski resorts. As conditions change, businesses that depend on reliable water supplies might also have to pay more for operations. The economic effects are not limited to local communities; they can also have an impact on national economies. For many parts of the world, the effects of the world’s glaciers receding on water availability are becoming an urgent concern.
Water cycles and the role of glaciers. As natural storage spaces, glaciers hold water in the winter and release it gradually in the summer. River systems that sustain hydroelectric power generation, drinking water supplies, and agriculture depend on this constant flow. Climate change’s effects on glaciers.
This balance is upset, though, by the glaciers melting more quickly as a result of climate change. As glaciers melt more quickly, some areas may initially see an increase in water flow; however, as glaciers continue to recede, this is frequently followed by a sharp decline. ramifications for ecosystems and communities. Communities that rely on glacial meltwater may eventually experience acute shortages during droughts or dry seasons. This change presents difficulties for ecosystems that depend on stable water levels for survival as well as for human populations.
Glacial retreat has an impact on global weather patterns in addition to local environments. Because they reflect sunlight back into space and affect atmospheric circulation patterns, glaciers are essential for controlling temperature and precipitation. As they deteriorate, their reflective capacity falls, which causes land and water bodies to absorb more solar radiation. Widespread changes in weather patterns may result from this change.
Once-cool regions might see warmer temperatures, for example, while other regions might see changed precipitation patterns that result in more rainfall or droughts. Wide-ranging effects on agriculture, water supplies, and the stability of the climate can result from these changes. It is crucial to comprehend these dynamics in order to forecast future climate scenarios and create successful adaptation plans. A comprehensive strategy combining adaptation and mitigation techniques is needed to address the problems caused by glacial retreat. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through sustainable land use, energy efficiency upgrades, and renewable energy sources is the main goal of mitigation initiatives.
Societies can contribute to slowing down the rate of global warming & the resulting effects on glaciers by reducing emissions at their source. As communities learn to deal with the changes that are already occurring, adaptation strategies become even more crucial. In areas impacted by shifting water availability, this can entail creating policies that support sustainable agricultural practices or making investments in infrastructure upgrades to better manage water resources. Community involvement in conservation initiatives can also be encouraged by increasing public awareness of the significance of glaciers and their function in regulating the climate.
In summary, glacial retreat is a complicated problem with broad environmental repercussions that go beyond the immediate loss of ice. The effects it has on wildlife ecosystems, societal structures, water availability, weather patterns, economic stability, and sea level rise highlight the urgent need for all-encompassing mitigation and adaptation strategies. The protection of both natural environments and human livelihoods in an increasingly uncertain future will depend on our ability to comprehend glacial dynamics as humanity struggles with the effects of climate change.