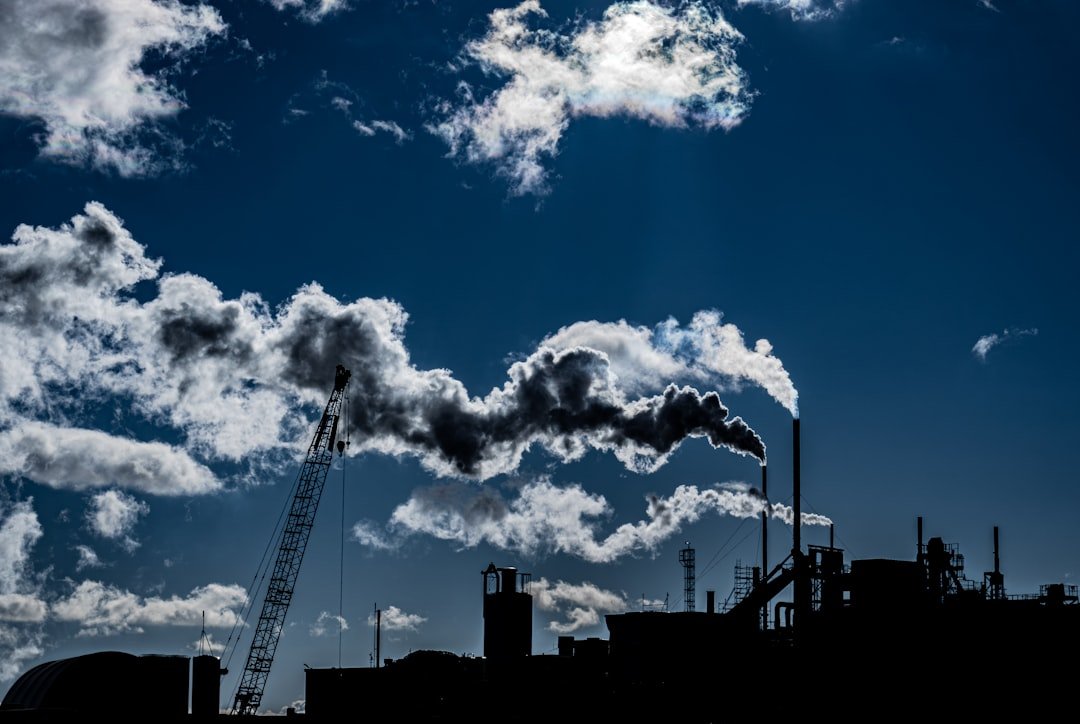
A Comprehensive Look at Air Pollution Air pollution is frequently characterized as an unseen danger that permeates the atmosphere and has an impact on the environment and human health. It speaks of dangerous compounds that can come from a variety of sources and manifest themselves in different ways in the air we breathe. These contaminants, which can negatively impact air quality, can be gases, liquid droplets, or solid particles. Air pollution is one of the biggest environmental health hazards, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), and it causes millions of preventable deaths annually. Because of its composition & the numerous contributing factors, air pollution is complicated.
Key Takeaways
- Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, such as particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone, which can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
- Common sources of air pollution include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, agricultural activities, and natural sources such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions.
- Air pollution can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even premature death, particularly affecting vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly.
- Environmental consequences of air pollution include damage to ecosystems, soil and water contamination, and the depletion of the ozone layer, leading to climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Measures to combat air pollution include the implementation of emission standards, the promotion of renewable energy sources, and the development of sustainable transportation systems, as well as international agreements and policies to reduce pollution levels.
Typical pollutants include carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Both natural events like wildfires and volcanic eruptions as well as human activities like industrial operations, automobile emissions, and agricultural practices can produce these substances. Since air pollution is a complex problem that requires immediate attention, understanding it necessitates a thorough examination of both its causes and effects. Determining the origins of air pollution is essential to creating efficient countermeasures.
Transportation, especially in cities with crowded car parks, is one of the main offenders. Large volumes of nitrogen oxides & particulate matter are released by cars, trucks, and buses, which worsens the quality of the air. This problem is made worse by the use of fossil fuels for transportation, since combustion engines emit toxic pollutants into the atmosphere. Air pollution is also significantly influenced by industrial activity.
Pollutants are frequently released by factories and power plants as a result of their operations. For example, sulfur dioxide and mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants are well-known for having detrimental effects on the environment & human health. Agricultural practices also contribute to air pollution by using pesticides and fertilizers that release harmful chemicals, including ammonia, into the atmosphere.
| City | PM2.5 Level (µg/m³) | Nitrogen Dioxide Level (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| New York | 12 | 0.03 |
| Beijing | 115 | 0.08 |
| Delhi | 180 | 0.05 |
By being aware of these sources, policymakers can put specific policies into place to lower emissions and enhance air quality. Air pollution has significant and wide-ranging effects on health. Numerous respiratory conditions, heart issues, & even neurological disorders have been related to exposure to contaminated air.
Particularly worrisome is fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which can enter the bloodstream and travel deep into the lungs. Research has indicated that prolonged exposure to PM2.5 can result in long-term health problems like lung cancer, bronchitis, and asthma. Also, those who are more susceptible to the negative effects of air pollution include children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing medical conditions. Because their respiratory systems are still developing and can be permanently harmed by exposure to contaminated air, children are particularly vulnerable. One cannot ignore the psychological effects of residing in polluted areas either; research has shown a link between elevated air pollution levels and higher rates of anxiety & depression in impacted communities. Therefore, tackling air pollution is a crucial public health issue in addition to an environmental one.
In addition to harming human health, air pollution has serious negative effects on ecosystems and biodiversity. The chemical makeup of soil & water bodies can be changed by pollutants, which can have a negative impact on both plants and animals. As an example, acid rain, which is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides reacting with water vapor, can seriously harm rivers, lakes, and forests. By reducing the pH of water bodies, this phenomenon damages aquatic life and upsets nutrient cycles. Also, by raising the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, air pollution can exacerbate climate change.
Global warming results from the trapping of heat in the atmosphere by carbon dioxide (CO2) & methane (CH4) emissions from industrial processes and agricultural practices. By altering species distribution and endangering biodiversity, this change in climate patterns has the potential to upset ecosystems. The relationship between environmental health and air quality emphasizes how urgent it is to address air pollution for the sake of both human well-being and the ecological balance of the planet. Governments and organizations around the world are putting various policies into place to lower emissions and improve air quality in response to the growing concern over air pollution. In the United States, regulatory frameworks like the Clean Air Act set limits on particular pollutants and set air quality standards.
These rules force industries to implement emission-reducing technologies & procedures. Many cities are also making investments in public transportation systems in an effort to lessen their dependency on private automobiles. Low-emission zone creation & the promotion of electric vehicles (EVs) are two initiatives that are becoming more & more popular as successful ways to reduce urban air pollution. The need for nations to pledge to cut greenhouse gas emissions is also emphasized by international agreements like the Paris Agreement, underscoring a global effort to address this urgent issue.
Government regulations are vital in the fight against air pollution, but individual acts also have a significant impact. Individuals can make a difference by incorporating more sustainable habits into their everyday routines. One way to drastically lower one’s own carbon footprint is to walk, bike, carpool, or take public transportation rather than drive. Local projects that promote clean energy sources like solar or wind power can also be supported by individuals. Also, educating local communities about air pollution can encourage group action. Participating in neighborhood cleanup events or pushing for more stringent emission standards can boost individual initiatives to improve the quality of the air.
Making small lifestyle adjustments, like using less energy at home or selecting goods with fewer volatile organic compounds, can have a big impact on air quality. Although there will be major obstacles to overcome, there are also encouraging advancements that could happen in the near future. Technological developments are opening the door to more effective industrial operations and cleaner energy sources, which could significantly lower emissions. Developments like carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology have the potential to lessen the negative effects of burning fossil fuels on the quality of the air.
However, if not controlled sustainably, ongoing threats to air quality come from industrial growth and urbanization. These issues are made worse by climate change, which modifies weather patterns that affect the concentration & dispersion of pollutants. As a result, enhancing air quality in the future will require a proactive strategy that blends strong legislative frameworks with technological innovation.
A thorough grasp of its causes and effects is necessary due to its extensive effects on ecosystems, health, & the climate.
Even though technological advancements and regulatory actions have resulted in significant progress, much more needs to be done. In the battle against air pollution, people are essential; grassroots collective action can support governmental initiatives to create cleaner environments. The significance of air quality for ecological balance and public health is becoming more widely recognized, making it evident that combating air pollution is not only an environmental problem but also a moral necessity for coming generations. Every effort matters in the fight for cleaner air for everybody, so now is the time to take action.
If you are interested in learning more about the causes of climate change and its impact on air pollution, you may want to check out this article on what causes climate change. Understanding the root causes of climate change can help us better address the issue of air pollution and work towards a more sustainable future. Additionally, exploring ways to maximize yields with climate-smart agriculture, as discussed in this article on maximizing yields with climate-smart agriculture, can also play a role in reducing air pollution and mitigating the effects of climate change.